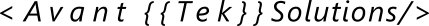
Distributed Ledger Platforms
de‑centralized Networks
- De-centralized peer‑to‑peer networks are essential for building and operating web 3.0 distributed ledgers and modern digital eco‑Spheres
- Nodes on P2P networks interact with each other directly. The use of intermediaries and middle‑men can be avoided
- With no middle‑men, transaction processing is streamlined and the state of the ledger can be viewed in real‑time from any node.
Distributed Ledgers
- Distributed Ledger Technology is key to processing information from the always‑on Internet of Things and is inspiring the creation of a wide wide range of other new innovative and disruptive services and eco‑systems.
Centralization ABC's
Legacy Systems on Centralized Networks
Nearly all the Web 2.0 online publications, e‑commerce, and social media platforms we use are centralized.
With centralized platforms
- All network activity flows to and from a single processing hub: typically a cloud platform or enterprise data center
- Databases and all other information repositories are controlled by the system's owner
-
The owning entity has control over all processing.
Your bank can decide to turn off its portal and online services will cease to exist for you and all other customers
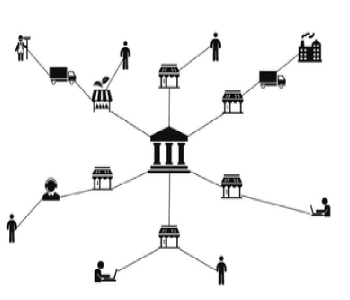
De-Centralized
A highly de‑Centralized peer‑to‑peer network is required for the operation of a digital ledger technology platform.
▪▪▪Anyone can set‑up a secure distributed node on a public digital ledger
▪▪▪
Out‑of‑the‑box DLT security and encryption protocols simplify setting‑up tamper‑proof processing environments with strong data integrity.
▪▪▪
Many DLT platforms cannot be public. They require secured services that can only be accessed by admins for managing the network and administering users and IOT nodes.
de‑Centralized / P2P Network
DeCentralized Networks and Digital Ledgers
A Perfect Fit
- Digital ledgers on de‑Centralized networks enable disintermediation ‑‑ a reduction in the use of intermediaries between producers and consumers. Benefits of disintermediation include: No single point of failure in the network, no central administrative authority, elimination of transaction fees
- DLT platforms are immutable. Once transactions are committed as ledger entries they are very hard to change, almost impossible. Data stored on the ledger is generally considered incoruptible
- Ledger platform protocols use advanced hashing and encryption methods to guarantee transactions and ledger entries cannot be tampered with during creation and are immutible after they become ledger entries. Encrypted digital signatures insure non‑repudiation ‑‑ the assurance that ledger object creators cannot successfully dispute ledger page or transaction authorship
The History
Distributed ledger technology [DLT] was introduced when the mysterious Satoshi Nakamoto published Bitcoin: A Peer‑to‑Peer Electronic Cash System in October 2008 only weeks after the collapse of Lehmann Brothers.
Two months later the Bitcoin Network went live on the Internet when a block of 50 bitcoins was “mined” by Nakamoto and sent to the computer scientist Hal Finney.
Today, the market cap of Bitcoin and the other top 100 crypto‑currencies that operate under the engineering principles of Nakamoto’s blockchain / peer‑to‑peer electronic cash system is approaching $250B.
The success of the crypto exchanges validated distributed ledger technology and created great excitement and interest re: the potential of DLT and de‑centralized networks.
In 2015 a huge advance in the capabilities of de‑centralized / blockchain‑powered platforms surfaced.
Ethereum ‑‑ a blockchain ledger with an integrated programming language was released.
“Smart contracts” extended Ethereum’s capabilities beyond the simple exchange of financial items and moved the Web 3.0 vision toward:
a more secure, trustworthy and globally accessible internet for agreements, finance, auditing, tracking and simple websites and web applications that use decentralized technology to overcome some of the practical, political and technological inefficiencies of previous approaches
Gavin Wood
The AvantTek Solution

